What is pagination?
If you’re also wondering the same, you have landed in the right place.
In this blog post, we’ll talk everything about pagination, what pagination is, how it works, and the best practices for making an SEO-friendly pagination for your website.
This post contains every single piece of information about website paginations (literally everything).
So, let’s not waste our time and jump right in.
Table of Contents
What is Pagination?
Pagination is the process of diving content into different pages to make it easy for the users to navigate the website without getting confused.
At the core, pagination is like having an organized librarian for your website content.
Instead of throwing all your web pages into a massive and messy pile, pagination neatly arranges them into manageable and identical sections.
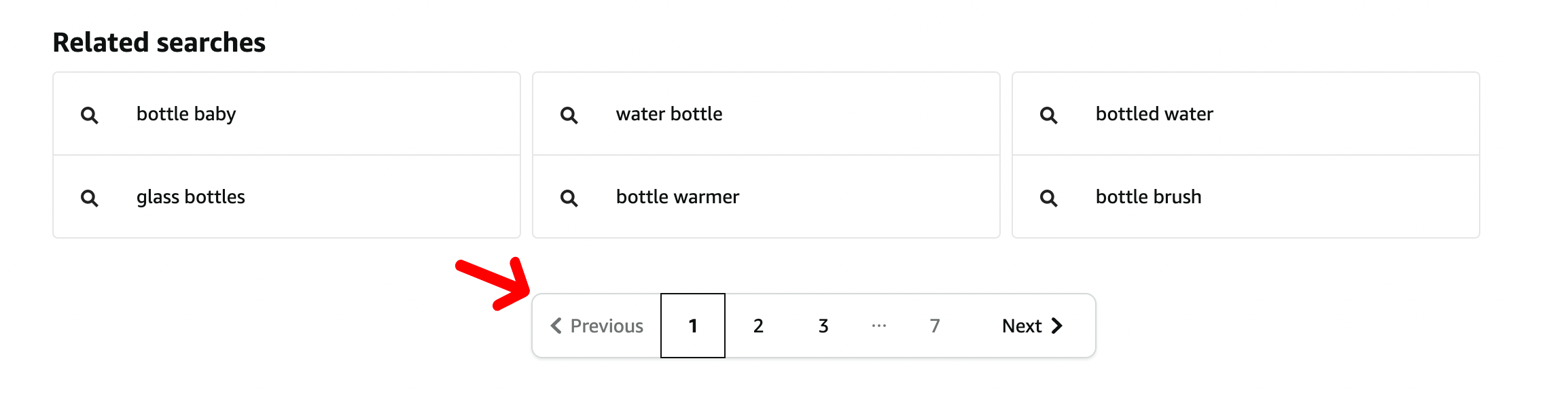
Here’s an example of pagination on our website.

Once someone clicks on the “Next” button or the following number, they will be redirected to the next page.
Here’s another example of pagination on Amazon’s website.
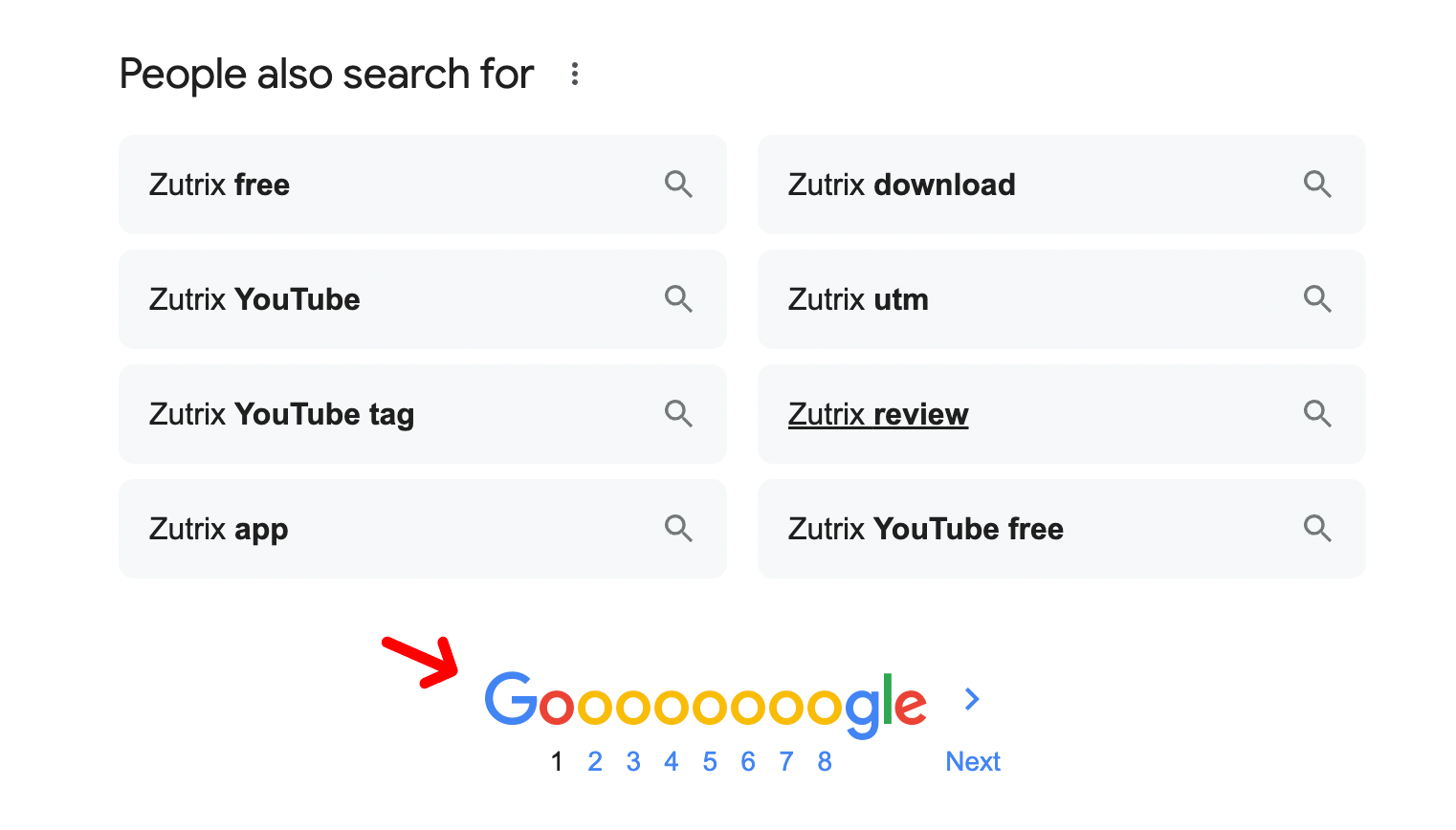
And here’s what Google’s pagination looks like (you might already have noticed this millions of times):
Not just Amazon and Google, but I can show thousands of other websites that use pagination to break down their contents into small chunks.
Almost the majority of the websites on the internet use this system.
But pagination isn’t just about slapping some numbers at the bottom of a page.
It’s a sophisticated system that makes life easier for users and website owners.
Pagination in websites can be used in plenty of different ways, such as for:
- Product catalogs.
- Blog post archives.
- Search result pages.
- Category archives.
- Image galleries.
- User-generated contents.
- Database records.
And more.
How Does Pagination Work?
Now we know what pagination actually is and how it looks.
But the real question that comes up now is, how does the pagination work on a website?
Let’s understand the technical side of pagination first (I promise I’ll keep it simple and easy to understand).
Behind the scenes, pagination works pretty systematically.
Firstly, the website counts how many items you have in total.
For example, let’s assume you have 100 blog posts where you want to use pagination.
Next up, you have to decide how many items you want to show on one page.
For example, you can show 10 blog posts on one page (all the blog posts will be divided into multiple pages using this same rule).
You can either list the pages in “last published date” order or manually change the position of your blog posts, as per your preference.
How Does Pagination Affect SEO?
Pagination is not only crucial for the user experience of a website, but it’s also quite vital for search engine optimization.
If done incorrectly, it can negatively impact your SEO performance and ruin your entire website’s reputation.
Here’s how pagination affects the SEO of any website:
Pagination Affects Your Website’s Overall Crawlability
Google’s crawlers set a limited crawl budget for every website. If your website has multiple contents, your crawl budget might get exhausted, and not all your web pages can be crawled and indexed.
Pagination helps them navigate content efficiently, ensuring more of your content gets crawled and indexed by Google.
Better User Engagement
When users can easily find what they’re looking for, they spend a longer time on your website and interact more with your content.
Longer website session durations are a strong ranking factor for search engines like Google.
In fact, a study by Backlinko found that websites with above-average on-site time tend to rank higher in Google compared to websites with lower session duration.
The study also revealed that the average time spent on a website for a Google first-page result is 2.5 minutes (based on 11.8 million Google searches).
Distributed Internal Links
Pagination helps to distribute link authority (link juice) across your pages more evenly.
This helps search engines understand your website’s structure, and due to distributed link authority, your search engine rankings improve.
Best Practices for SEO-Friendly Pagination
Most people don’t pay attention to making their website pagination SEO and user-friendly.
But that’s a big mistake.
Pagination plays a crucial part in search engine optimization, and it should be appropriately optimized to achieve the most optimal results.
Here are some of the easy things you could do to make your website’s pagination SEO and user-friendly:
1. Ensure The URLs Are Clear
Ensure the URL of your paginated contents is clear and easy to navigate for the search engines.
Earlier, SEOs used the “rel=prev/next” attribute to notify search engines about the relationship between the paginated contents.
However, a few years ago, Google retired this attribute, making it difficult for search engines to identify paginated content.
One way to fix this is to use a clear and unique URL structure to help search engines determine the correct order of your paginated content.
Here’s what good URLs look like:
- example.com/blog/page/2
- example.com/products?page=3
- example.com/category/shoes/page-4
And here’s what to avoid:
- example.com/blog?p=2&sid=123&sort=date
- example.com/products?pgid=4&view=grid
- example.com/category?page_id=5&session=abc
2. Do Not “NoIndex” Your Paginated Contents
One of the common mistakes that most people make is adding a “noindex” tag on their paginated pages.
But you shouldn’t do this for three main reasons:
- Firstly, no-indexing paginated pages prevents search engines from discovering new content on your website.
- It can break the flow of link juice throughout your website.
- It makes it difficult for search engines to understand your website’s structure.
Always allow search engines to crawl and index your paginated pages naturally. This helps them better understand the relationship between the contents.
3. Don’t Optimize Paginated Pages
While we strongly recommend letting search engines index your paginated pages, we also highly recommend not optimizing them so that they don’t clash with the main content for the targeted keyword.
It confuses the search engine.
Hence, it’s better to leave it as it is without any keyword optimization.
5. Use Self-Canonical Tags on Paginated Pages
Each paginated page should canonicalize itself.
When you self-canonicalize your paginated pages, you’re essentially notifying Google that each “paginated page” is the main version of the content.
If you don’t self-canonicalize each page, search engine crawlers will see all the pages as similar and might get confused about the primary content.
Conclusion
Pagination might seem like a small website feature that no one really cares about, but it’s one of the most crucial elements of user experience and SEO.
If done right, this small change can make a huge difference in how users and search engines interact with your content.
Whether you’re running a blog, e-commerce site, or any content-heavy website, well-planned website pagination can significantly improve your user experience and SEO performance.