Struggling to get your website indexed on Google?
You’re not alone.
Every website owner and SEO professional must have experienced this at least once in their lifetime for every website.
And it’s an extremely important issue that should be fixed as soon as possible if you want to get traffic from Google.
But the question is: Why are your pages or website not getting indexed by Google?
There could be multiple reasons for which you’re experiencing Google page indexing issues on your website.
In this post, we’ll show you some common Google indexing problems that might be stopping Google from indexing your website.
So, let’s understand what could be causing this indexing issue and how you can solve it quickly.
Table of Contents
What Is Google Page Indexing Issue?
But before we see the reasons for which indexing issues occur, let’s first understand what the Google indexing issue actually is.
Google indexing issues refer to a scenario when Google algorithms either have difficulties crawling your page or can’t crawl at all.
In that case, Google doesn’t have any other choice than to ignore your page.
And for that reason, your page doesn’t get indexed and included in the SERP by Google.
The main job of Google is to crawl websites, understand the context of the page, and rank them on the SERP based on the page’s relevance to the keyword and various other ranking factors.
But if Google can’t even crawl your website properly and constantly gets any kind of error or restriction, they won’t even bother to index your page, no matter how well-optimized your content is or how many backlinks you’ve built.
So, if you notice any indexing problem within your website, your first and most important priority should be fixing that issue ASAP.
But how can you find out if your website has any Google indexing issues?
Well, luckily, Google provides a free tool called “Google Search Console,” where you can see every indexing issue your website is currently experiencing.
And the best part?
Google itself will provide all these data without any third-party intervention.
How to Detect Indexing Issues on Your Website
Detecting page indexing issues is super easy.
You don’t even have to do any hard work. Google already gives you all the data you would need to find and fix the indexing issues on your website as quickly as possible.
To detect page indexing issues, head over to your Google search console.
If you have not verified your website with Google Search Console yet, you would need to verify it first and wait for a couple of ways until you get this data.
But if you already have a Google search console verified website, here’s what you have to do:
Step 1. Click on “Pages” from the left sidebar under the “Indexing” section.
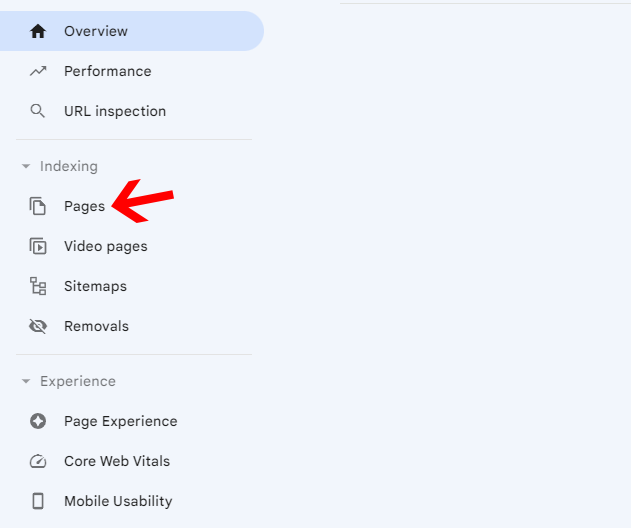
Step 2. Now, scroll down until you see a section called “Why pages aren’t indexed.”
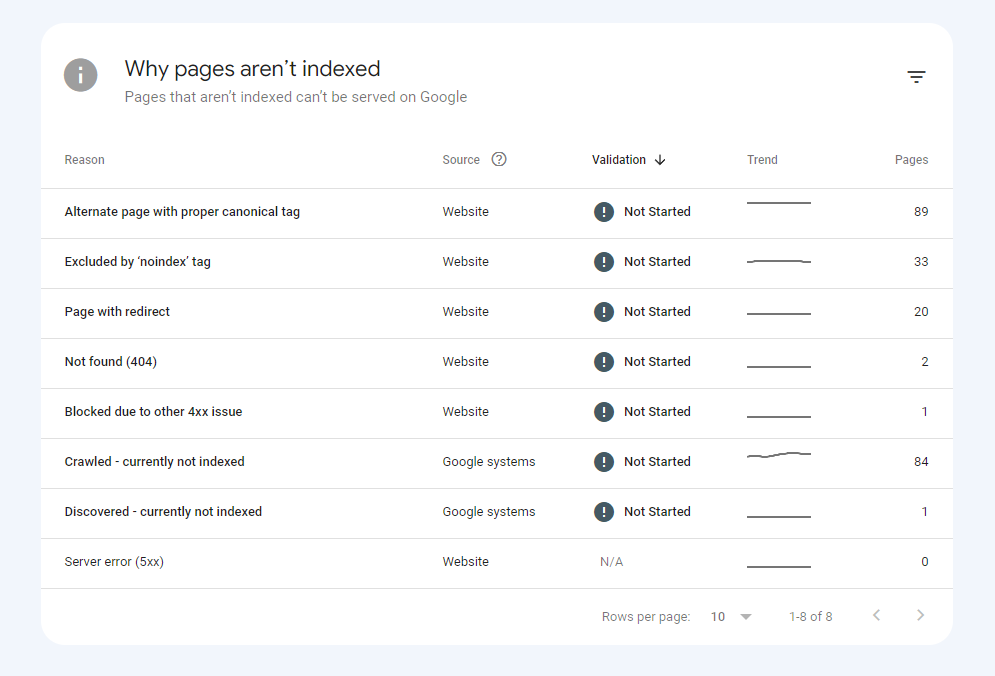
Within the section, you’ll be able to see why certain pages on your website aren’t getting indexed by Google.
Then, you would have to go ahead and fix the pages based on the indexing issue those certain pages are having.
And once you fix that, just click on the “Reason” and tap on “Validate Fix.”
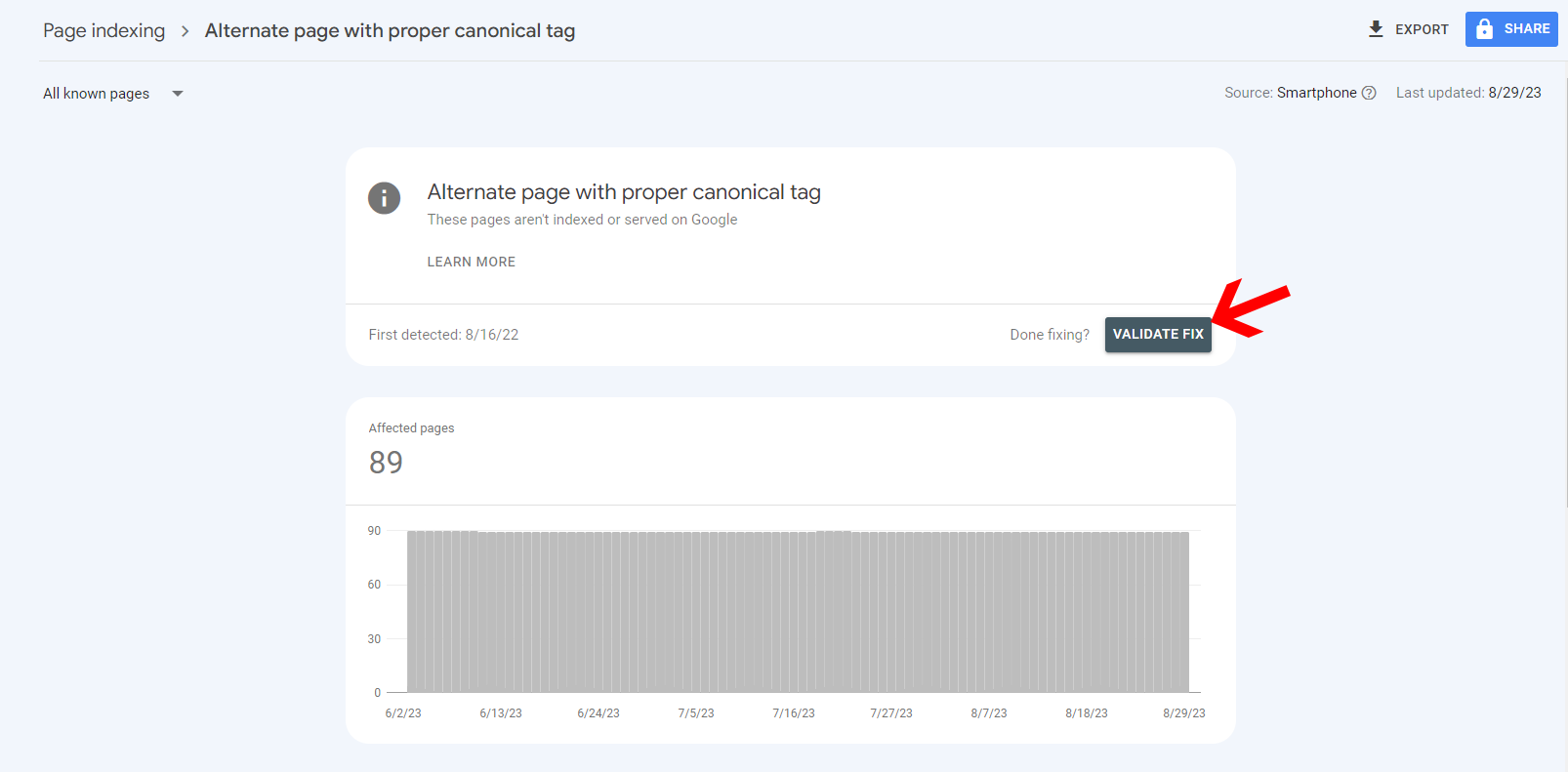
It will send a signal to Google crawlers that you have fixed the issue so they can again try to recrawl those pages.
But remember that not all indexing errors are bad for your website.
In fact, some Google indexing errors like “Excluded by ‘noindex’ tag” and “Alternate page with proper canonical tag” are some of the most common errors that every website has that there’s nothing to worry about most of the time.
Sounds confusing?
Don’t worry.
Later in this post, we’ll describe why you’re getting these errors and how to fix page indexing issues the right way.
10 Most Common Google Indexing Issues And How to Fix Them
1. Error 404 Not Found
So, here comes the most common and most dangerous indexing issues that can seriously destroy your website’s SEO and drain away all your hard work if not noticed.
Error 404, also known as a broken link, refers to a situation when Google bots try to crawl the page but cannot find any content within the page, and the page returns a 404 status code.
This indexing issue can occur when you have deleted a page from your website but haven’t removed it from the sitemap.
Apart from that, if you have changed or renamed the URL of a particular page without updating it to your sitemap and redirecting your old URL to the new one, this indexing issue can occur as well.
To fix this indexing issue, all you have to do is update the sitemap whenever you remove or make changes to a particular URL and set up proper redirection.
2. Soft 404 Error
A soft 404 error occurs when a page returns a 200 OK response, but Google considers it as 404 as the crawls couldn’t find any content within the page for some reason.
This confuses the Google crawlers and makes the situation even worse.
This error can happen due to multiple reasons like poor content within the page, no proper redirection, incorrect server configuration, or CMS issues.
To fix this issue, the most important thing you would have to do is set up proper redirection if you’ve deleted or moved certain pages.
If you don’t have any alternative pages for redirection, make sure to mark it correctly as a 404 error so that it doesn’t confuse the search engine crawlers.
On top of that, make sure your server is configured properly, and your CMS is not having any kind of internal issues.
3. URL Blocked By Robot.txt
If you’re getting an indexing error on your Google search console named “Submitted URL blocked by robots.txt,” this means you may have blocked certain pages on your website using robot.txt.
Google crawlers won’t be able to crawl if you block those pages using robot.txt, and eventually, it won’t get indexed as well.
If it’s intentional from your end, you can skip this.
But if you have not blocked any pages using the robot.txt but still you’re getting this error on your search console, it’s better to check your robot.txt file.
You can edit and reupload the file again if you find any unusual restrictions within the file that you have not placed.
4. URL Marked as “noindex”
This error indicates that some pages on your sitemap were marked as “noindex,” but either you have tried the manual index request, or it’s in the sitemap.
If that page is important for your site and you want Google to crawl and index it, just simply remove the “noindex” tag from that page.
For custom CRM, you would have to change it manually, but if you’re a WordPress user, you can use your SEO plugin to remove the “noindex” tag from that page.
And on the flip side, if you don’t want Google to index certain pages and you have added the “noindex” tag to those pages, just remove them from your sitemap.
5. Redirect Error
Redirect error means Google bots couldn’t reach the redirected destination, and they have encountered an error.
This error can occur due to multiple reasons.
For example, your redirect chain could be too long, your redirection could contain an empty URL or a redirect loop.
Whatever the reason is, the only way to fix this issue is by manually fixing the redirections on your website.
Make sure the redirects on your website are set up properly to avoid all the possible reasons for any sort of redirect errors.
6. Discovered But Currently Not Indexed
As the name itself suggests, if you’re getting this error on your page, “Discovered – Currently not Indexed,” it means Google is aware of your page but still hasn’t indexed it yet.
This issue generally happens within larger websites with too many pages due to over-usage of the crawl budget.
Crawl budget basically is how many pages and how quickly a search engine like Google wants to crawl your site.
If you have a small or mid-size website, it won’t be an issue for you, and your pages will eventually get indexed within a few days.
But for larger websites, you may have to look for ways to optimize and fully utilize your crawl budget so you don’t get into these issues in the future.
7. Crawled But Currently Not Indexed
If you’re getting “Crawled – currently not indexed” status on your Google search console, this means Google has crawled your page but chose not to index it due to some reasons.
Remember, Google generally doesn’t index all the URLs on any given website. So, occasionally, you might see a few pages on your site showing this status.
But if you get this too often or on your important pages, this could be a massive issue for you.
This status shows up on the search console mostly due to reasons like:
- Site-wide content quality issue
- Duplicate content
- Poor website structure
Now, to fix this, all you can do is:
- Publish more quality content on your website
- Improve your website structure
- Remove duplicate contents
- Internal link your website properly
Still, the decision for indexing your page will depend upon Google. They may or may not choose to include the page in the future.
8. Server Error (5xx)
The server error (5xx) is not an issue from Google’s end.
It’s an issue on your own website.
If you see “Server Error (5xx)” on your GSC report, this means when Google tried to crawl your website or certain pages, they encountered a server error.
As a result, they were unable to crawl the site and index it.
One of the most common reasons for this server error (5xx) could be a coding error within the backend code of your website or CMS.
If you’re a developer yourself, you already know how to fix it.
But if you’re not, you might need some help from developers to see if everything is right within your website’s code and what may be causing that issue.
9. Blocked Due to Unauthorized Request (401)
Blocked due to unauthorized request (401) means that a specific page requires login credentials (like email and password) to be able to view the content of the page.
And since Google bots don’t have any login credentials to that page, they just simply can’t crawl it.
So, if you want Google to crawl and index that page, you would eventually have to lift the password protection.
But if it’s not necessary for you to index that page, leave it as it is.
10. Blocked Due to Access Forbidden (403)
Blocked due to access forbidden error means Google crawlers cannot crawl your website because your server responded with a “403 Forbidden” HTTP status code denying Google bot from accessing your site.
This can happen due to various reasons like permission issues, password-protected pages that require authentication, IP blocking, and security plugins.
Conclusion
So, these are some of the most common Google indexing issues you might face on your website.
To check whether your website is currently facing any indexing issues, you can check the indexing report Google Search Console.
You should regularly audit your website and check for any errors on Google Search Console.
So that if there is any error coming up, you can fix it quickly and save your website from any harm.